Every modern person at least once in his life has encountered the problem of parasites in the body.The quantity and variety of parasites, which, in the literal sense of the word, cannot live without us, are simply huge.Parasites in the human body use it as a source of food and habitat until they completely exhaust it, but without giving out their presence.
Parasites are microscopic sizes or can grow up to several meters in length, but even in this case, their vital activity in the body can not always be felt.A person, as a rule, does not feel them and does not even know about their presence within himself.Meanwhile, they are able to live in a human body for years and even decades, causing him irreparable harm.
Parasites in the human body pose a serious danger and pose a great threat to human health, since they violate the work of internal organs and systems, provoke a failure in the work of the immune system and interfere with the complete assimilation of useful substances, vitamins and minerals.In some cases, the situation is so serious that it can even lead to death.
Types of relationships between organisms
In nature, there are several types of relationships between organisms that have a diverse effect on each other.
The impact of one species on another can have both neutral or positive, and negative.
In addition, there are different combinations of such relationships.Distinguish:
- symbiosis;
- neutralism;
- antibiosis.
Symbiosis is a form of relations between two organisms, from which both benefit.
Neutralism is a type of biological connection, which consists in the inhabitation of two organisms in one territory, but at the same time they are not related to each other and do not directly affect each other.
Antibiism is an antagonistic type of biological relationship in which one type of population limits the possibilities of another, adversely affecting it.One of the most negative types of antibiism is parasitism.
Parasitism and parasites
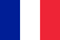
Parasitism is a form of antibiotic in which representatives of one species use the body of another species as a temporary or constant environmental environment and a source of nutrients.
Biological organisms that live at the expense of another organism are called parasites.
Parasites do not kill their owner, but for a long time use it as a source of food and habitat.
The parasites include:
- parasitic worms;
- pathogenic bacteria;
- protozoa;
- mushrooms;
- Viruses.
The host organisms can be:
- bacteria;
- protozoa;
- plants;
- animals;
- Human.
In the process of development, parasites pass several stages of development from eggs and larvae to adults (sexually mature, invasive), which indicates their long -life and need to change 2-3 owners.
Classification of parasites
All parasites are divided into bond and optional.
Oblige parasites outside the host’s body either die or exist in an inactive state.For example: viruses.They lead an exclusively parasitic lifestyle, that is, they completely depend on the owner and activate their activities within it.
Optional parasites lead a parasitic lifestyle, but if necessary, can exist in an absolutely normal form in the external environment.For example: pathogenic mushrooms and bacteria.
By the nature of the relationship with the host body, they share:
- true parasites;
- false parasites;
- Super parasites.
True parasites are the same bond parasites for which a parasitic lifestyle is the only form of survival.However, there are parasites that can be either bonding (constant) and optional (temporal).For example: lice, fleas, intestinal helminths.
False parasites - voluntarily living organisms, which, in case of accidentally entering the body, are able to live in it for some time and harm it.For example: larvae of a room fly in a person’s intestines.
Super parasites are parasites living in other parasites.For example: bacteria and viruses in other parasitic insects that live in other organisms.
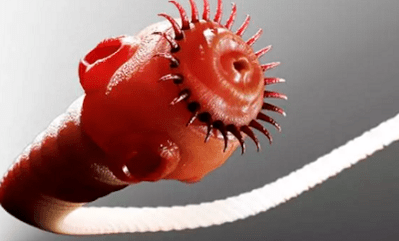
Depending on the duration of interaction with the host body, they distinguish:
- constant parasites;
- temporary parasites.
Constant parasites are organisms that conduct their entire life cycle in the body - the owner, putting down the larvae in it.For example: ascarides, tapeworms, lice.
Temporary parasites;Live and eat at the expense of the owner at a certain stage of development.For example: larvae of a volt-fart fly and an Imago (adult insects)-in fleas and mosquitoes.
At the location of the host body, the parasites are divided into:
- ectoparasites;
- Endoparasites.
Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the skin of the host body.For example: lice, fleas, ticks.
Endoparasites are organisms that are located inside the host body.Endoparasites are divided into:
- internal parasites;
- tissue parasites;
- intracellular.
Intra -capture parasites are organisms that are located in cavities connecting to the external environment, for example: ascaris, Vlasov -headed in the human intestines.
Fabric parasites-a type of organisms that are located in closed cavities and tissues of the host body, for example: for example, liver bacon, cystics of tape worms.
Intracellular parasites are localized in the cells of the body - the owner, for example: malaria plasmodia, toxoplasm.
In terms of distribution in the environment, parasites are:
- Curly, encountered everywhere;
- Tropical, which are common only in hot, tropical climate.
According to biological and epidemiological characteristics, parasites are divided into:
- Geogelminters- these are parasites that initially undergo developmental stage in the human body, and then in the external environment (for example, Earth);
- Biogelminters- parasites in which the development cycle takes place not only in the human body, but also in the organisms of other creatures.A person, as a rule, is the final owner, and sometimes intermediate.
- Contact helminthsThey are distinguished from the host’s body by already mature or half -mature, as a result of which it is possible to repeat its infection or infection of another person (autoinasia, reinvasia).
How parasites fall into the human body
There are many favorable factors that contribute to the entry of parasites into the human body:

- dirty hands;
- animal hair;
- poorly cooked products (alimentary factor);
- contact-household factor;
- transmissible;
- percutant.
Dirty hands are the main source of infection with parasitosis.There are a number of diseases called "diseases of dirty hands."Larvae of worms, falling on first on the skin of the hands, and then in the mouth, cause characteristic symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract.The transmission path of these infections is called fecal-oral.Thus, helminths with contact helminthiasis fall into our body.For example, ascaride eggs enter the human body through dirty hands, poorly washed vegetables, fruits, berries, greens, and are also spread to flies.
Animals and their wool are a source of Ascaride and Liphyli with worms.For example, for a long time, which has fallen from the animal’s wool, retain vitality (up to about 6 months) and, falling on carpets, things, bedding, children's toys and hands, penetrate the food tract.
Also, through wet breathing, dogs and cats are able to dissipate parasite eggs at a distance of 3 - 5 meters.In addition, there are fleas on the wool of dogs and cats, which also tolerate worm eggs.
The alimentary method of infection with parasites is carried out:
- through poorly washed vegetables and fruits;
- poorly cooked food (most often meat);
- Infected water.
For example, incorrectly cooked barbecue, jerky or homemade lard can infect a person with trichinellosis and echinococcus, and poorly cooked dry fish or caviar can cause an infection with an opisthorchiasis and a wide tape.
The transmissive method of infection occurs using blood -sucking insects, for example: ticks, mosquitoes, lice, fleas, bugs.
Contact - the domestic path of infection is carried out through an infected person or animal, when contacting or using common household items.
The percutant method of infection occurs during bathing in reservoirs or in contact with infected soil.Larvae penetrate the body through the mucous membranes or human skin during contacts with water or infected soil.
Features of the device
Almost all parasites are highly adaptable to survival.There are a number of factors that contribute to their high vitality:
- A long life expectancy.For example, helminths live in the human body for years, and sometimes exactly as much as the owner lives.
- Helminth eggs are able to persist and not collapse in the external environment for decades.
- The stage of development of the parasite also contributes to its life expectancy.It passes all the stages of development, starting from the egg, continuing the larva and change of the owner, in case of lack of nutrients.
- The ability of parasites to cause a state of immunodeficiency in the owner, which allows you to penetrate pathogenic agents from the outside, as well as "incite" dormant internal infections.
- Helminths that fall into the gastrointestinal tract of a person produce anti -enzymes, which allows them to pass their own death, but at the same time they violate the normal process of eating and cause toxico - allergic reactions in their host: asthma, urticaria, dermatitis.
- The invulnerability of parasites is associated with the exchange of genetic information during sexual reproduction, which leads to the stability of their heterogeneous population.
- The wide vitality of helminths in many habitats: soil, water, animals, plants.
- The lack of effective methods of immunoprophylaxis, since parasites are able to suppress or modify the immune response of the host body.
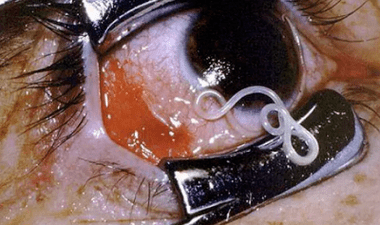
How to identify parasites in the body
As a rule, a person asks such a question when his health is thoroughly undermined.It is common for a person to dismiss the problem at its initial stage until it develops into a serious form and will affect his well -being.
Since parasites are divided by the habitat in the body - the owner into endoparasites and ectoparasites, the symptoms are divided into internal and external.
Ectoparasites are characterized by a certain activity, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- skin rashes;
- itching;
- burning;
- hyperemia;
- pain (if it was a bite);
- the presence of a wound at the place of a bite.
Detecting endoparasites is much easier.The following actions are carried out for this:
- visual identification (if there is penetration from the outside through the skin);
- Microscopic examination.
The discovery of ectoparasites is a difficult task, since in the process of evolution the “dependents” have adapted to survival, while disguising and without betraying themselves, they conduct destructive work in the host’s body.After all, a person lives, for example, with worms since its appearance, and the stages of their development can take from several months to a decade.So how to determine the presence of parasites in the body?
External and internal manifestations
Since parasites differ in a long life expectancy and actively multiply in the human body, they cause symptoms that are long -term recurrent and chronic.
The external manifestations of parasite activity include:
- skin rash;
- itching;
- burning;
- hyperemia;
- feverish condition;
- Quincke's edema.
It is important to know that the degree of allergy development depends on many factors:
- location of the parasite in the body;
- parasite contact with tissues and vital organs;
- the amount of produced toxins.
The following symptoms include violations in the body of internal invasion:
- disorders in the work of the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, diarrhea, belching);
- weight fluctuations associated with a lack of nutrients and a decrease in appetite;
- craving for sweets due to metabolic disorders and general weakening of the body;
- chronic fatigue syndrome, which is manifested by general fatigue, drowsiness, in some cases insomnia, impaired concentration and memory;
- constant headaches caused by weakness of the body and intoxication;
- grinding teeth in a dream (bruxism), is especially manifested in children;
- swelling of the limbs;
- nervous disorders and psychic disorders, since parasites can cause depression and irritability;
- paroxysmal cough;
- muscles and joint pain;
- painful pallor of the skin;
- skin lesions (dermatitis, eczema, acne and acne).
It is especially important to know the general symptoms that are observed with intestinal parasitic invasion.
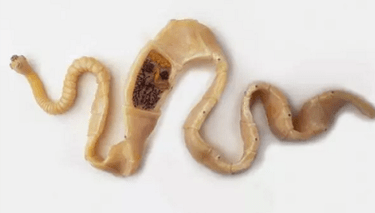
Violations in the digestive tract, which are manifested by the following symptoms:
- intestinal cramps;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- flatulence;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- Changing the color of feces;
- itching in the anus;
- Visual detection of helminths;
- The presence of worms in the gag.
Since worms can reach significant sizes in the body, they are able to physically complicate the progress of feces and violate the work of other organs, for example, the bile ducts.
Parasites can cause violations in the work of a particular organ or system.
The most common violations are:
- Anemia.
- Lesions of the central nervous system.
- Abscesses in the liver.
- Purulent inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas.
- Fruits in the work of immunity, up to the development of autoimmune reactions.
- Disorders in the operation of the respiratory system.
- Joint diseases.
Diagnosis of parasites
All of the above symptoms cannot always accurately confirm the presence of parasites in the body, since this symptoms can be observed with many diseases.
You can establish the presence of parasites in the human body when examining feces.However, this method is unreliable, because the parasite larvae can not always be seen through a microscope or skip them.In addition, not all parasites lay many eggs.
In order to detect parasite larvae in feces, it is necessary to take up to 8–10 times a fecal analysis.But if in this case the analysis did not show anything, but the doctor has doubts, then a number of serological blood tests are prescribed, which will help detect antibodies of helminths that appear in the blood a few weeks after infection with parasites.

There are other methods for identifying the “dependents” the so -called string test.A string with a capsule is inserted into the intestines through the nose and removed it after four hours along with the samples received.
Another method is a colonoscopy during which the specialist considers the condition of the inner surface of the colon using a special probe.
Specialists found that the most common parasites are helminths.In addition, they are all very viable and fertile, and their goal is to destroy their master and extract maximum benefits for themselves.
How to remove parasites from the human body
It is difficult to get rid of parasites, but it is possible.It is important to prioritize: it is necessary not only to know how to get rid of parasites, but also to understand what the treatment process itself is.It is carried out in three directions:
- The destruction of parasites at all stages of existence.That is, it is necessary to destroy not only adults, but also larvae and their eggs.
- Normalization of the work of all organs and systems of the body.
- Restoration of the body.
To satisfy all three of the above items will help modern drugs based on plant components that the specialist will prescribe.
Such drugs are modern drugs and have a certain therapeutic effect.The use of these drugs in the complex allows you to combine their therapeutic effect and get a wonderful result.
Dosage and combination of drugs with each other is carried out on the basis of:
- stages of parasitic invasion;
- general condition of the patient;
- the availability of complications from a certain body;
- severity of the course of the disease.
The priority of anthelmintic drugs is based on:
- efficiency;
- security;
- The possibility of combining several drugs for the best therapeutic effect.
Treatment with folk remedies is a very effective way to get rid of parasites.Most often, grass cleansing tea is used, which neutralizes the harmful effect of parasites, cleanses the liver and gall bladder.
They prepare tea as follows: take one tablespoon of the following plants each: oak bark, buckthorn, wormwood, tansy.Then, one tablespoon of a plant mixture is poured with 500 ml of boiling water and left in a closed dish overnight.In the morning, on an empty stomach, 100 grams of the resulting tincture are drunk.Treatment continues for two to three weeks.
Pumpkin seeds are also very effective in the fight against parasites.To get rid of parasites, 300 grams of pumpkin seeds are taken, they are cleaned of the peel, but at the same time they leave as much transparent film as possible, which envelops the seeds.Seeds must be eaten in the morning on an empty stomach.This recipe eliminates not only parasites, but also improves the functioning of the intestines, stomach, liver and gall bladder.